深入淺出 pinia(二):createOptionsStore
Pinia 是目前 Vue 官方首推的狀態管理工具。這個系列分享不會特別著重於如何使用 Pinia,而是深入剖析 Pinia 的原始碼,研究它的設計,從中吸收寶貴的經驗。在上一篇內容中,我們先查看了 Pinia 實例上的成員,也初步了解了 defineStore 的功能。接下來,我們將更深入地了解 Options Store 內部的實作。
前言
本篇的 pinia 版本為 2.1.3
這系列一共有三篇文章,分別是:
如果你有使用過 Vuex,或者還沒有接觸過 Composition API 的話,Options Store 應該是比較好上手的一個選擇,這也是官方建議可以優先嘗試看看的方式。
本篇將聚焦在 Options Store 的實作細節。
Options Store
在第一篇中我們了解到,如果選擇了 Options Store,在 useStore 內會使用 createOptionsStore 來建立 Store instance。在 Pinia 中,Options Store 和 Setup Store 並不是完全分開處理的兩段程式碼,反而是在 createOptionsStore 內部會呼叫 createSetupStore 來完成 Options Store 的建立。
function createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia) {
const { state, actions, getters } = options
// 整理出 setup function
function setup() {
//
}
const store = createSetupStore(id, setup, options, pinia, true)
return store
}
為了更清楚地了解我們必須如何整理出 createSetupStore 需要的資料,我們需要先認識 Setup Store 的定義方式:
const useStore = defineStore('SETUP_STORE', () => {
// `Ref` 表示是 state
const count = ref(1)
// `Computed` 表示是 getter
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2)
// function 表示是 action
function addCount () {
count.value++
}
return {
count,
doubleCount,
addCount,
}
})
在 Setup Store 中,Ref 和 Reactive 被視為 state,Computed 被視為 getter,而 function 被視為 action。因此,我們接下來要完成 Options Store 的步驟如下:
- 將 state 整理成
Ref。 - 將 getter 整理成
Computed。 - action 不需要特別處理。
我們將一步一步完成 Options Store 的實作。
取得 state
在使用 Options Store 時我們需要定義一個 state function,並且回傳一個物件。
export const useStore = defineStore('STORE_ID', {
// ⬇️ 我們定義的 state function
state: () => {
return {
count: 0,
name: 'Eduardo',
isAdmin: true,
items: [],
hasChanged: true,
}
},
// ...
})
因此我們可以透過執行 state function 來取得 state 物件。取得 state 物件後我們把這個物傳給 pinia.state.value[id]。
function createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia) {
const { state } = options
function setup() {
if (isVue2) {
// Vue 2 的設計必須使用 `set` 對響應物件添加屬性
set(pinia.state.value, id, state ? state() : {})
} else {
pinia.state.value[id] = state ? state() : {}
}
const localState = toRefs(pinia.state.value[id])
}
}
在第一篇我們知道 pinia.state 是一個 Ref 的物件,所以當我們再透過 pinia.state.value[id] 將剛剛傳的 state 時,這個取出的 state 會變成一個 reactive 化的物件。
因為我們最後要把這個 state 傳給 createSetupStore 使用,所以我們需要將裡面每一個屬性都透過 toRefs 轉換成 Ref。
// 這裡得資料是一個 Reactive ⬇️
const localState = toRefs(pinia.state.value[id])
// ⬆️ 這裡會變成一般物件,裡面的資料都是 Ref
到這裡 state 就差不多初始化完畢了!
整理 getters
我們來看看 Options Store 的 getters 是怎麼定義的:
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('STORE_ID', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
// getter 會接收 state 當作參數,或是透過 `this` 來取得 state
// ⬇️ Options API 的 getters
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
// 也可以透過 `this` 來取得 state
tripleCount() {
return this.count * 3
},
},
})
根據這個範例,我們可以知道 getters 是一個物件,裡面的每個屬性的值都是一個 function,這些 function 會接收 store 當作參數,或是透過 this 來取得 store。
所以我們需要講 getters 轉換成 Computed,並且把 store 傳進去。
function createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia) {
const { getters } = options
function setup() {
// ...
const localGetters = Object.keys(getters || {}).reduce((computedGetters, name) => {
computedGetters[name] = markRaw(
computed(() => {
const store = pinia._s.get(id)
// store._r 的註解:
// Vue 2 only. Is the store ready. Used for store cross usage.
// Getters automatically compute when they are added to the store,
// before the store is actually ready, this allows to avoid calling
// the computed function yet.
if (isVue2 && !store._r) return
return getters![name].call(store, store)
})
)
return computedGetters
}, {} as Record<string, ComputedRef>)
}
}
我們可以透過 Function.prototype.call 來改變 this 的指向,所以在每一個 getter function 內可以用 this 或是第一個參數,來取得 state。
// ⬇️ 指定 this 的指向為 `state`
fun.call(thisArg, arg1, arg2, ...)
// ⬆️ 第一個參數 `state`
這樣 getters 就整理完畢了!
合併 state、actions 跟 getters
我們有了 state 也整理了 getters,我們可以把他們跟剩下的 actions 合併起來,從 setup 這個 function 中回傳。
function createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia) {
function setup() {
return Object.assign(
localState,
actions,
getter
)
}
store = createSetupStore(id, setup, options, pinia, true)
}
這樣我們就完成了 createOptionsStore 的實作了!
解決 Server Side Render 的問題
Server Side Render 會遇到什麼問題?我們先看看 Server Side Render 的流程:
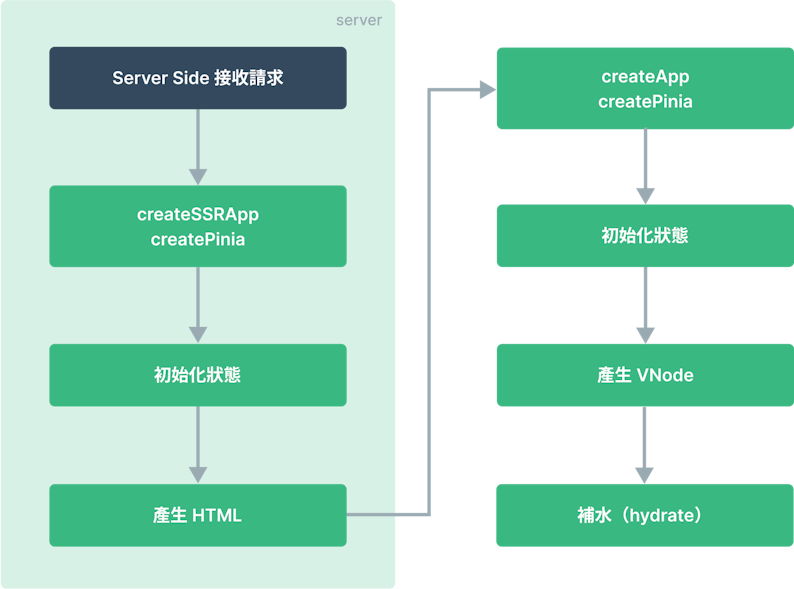
我們可以看到在 Client 端執行到最後會進行進行補水(hydrate),什麼是補水?
當我們接收到 Server 端產生的 HTML 檔案這個 HTML 是純靜態的,Vue 並沒有辦法直接操作這個 HTML,所以我們需要透過 hydration 將這個 HTML 轉換成 Vue 可以操作的 DOM。
在補水的過程中如果遇到 Server 端與 Client 端產出的 HTML 結構不相符的話,就會出現 hydration error 的情況。這通常表示 Server 端和 Client 端之間的元件或狀態存在不一致的情況,例如:
const useStore = defineStore('OPTIONS_STORE', {
state: () => ({
env: process.server ? 'server' : 'client',
}),
})
const store = useStore()
store.env // hydration error
所以我們只要想個辦法讓 Client 端的 Store instance 在初始化時取得跟 Server 端一樣的 state,這樣就可以確保 hydration 不會因為狀態對不起來而出錯。
具體該怎麼做呢?
我們可以在設法將 Server 端最終存在 Pinia instance 上的 state 隨著 HTML 傳到 Client 端,並且在 Client 端執行 createPinia 之後,將 state 寫回 Pinia instance 的 state 裡面。
const app = createApp()
const pinia = createPinia()
app.use(pinia)
if (import.meta.env.SSR) {
// ⬇️ 這個物件將被轉換成字串並設置為 window.__PAYLOAD__
payload.pinia = pinia.state.value
} else if (nuxtApp.payload && nuxtApp.payload.pinia) {
pinia.state.value = payload.pinia
}
而原本取得 state 的地方需要判斷 Pinia instance 上有沒有從 Server 端帶來的資料,如果 Pinia instance 上已經存有對應 store 的初始 state 那就會沿用這個 state 而不會透過 state() 取得新的 state。
因此上面取得 state 的程式碼就會變成:
function createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia) {
const { state, actions, getters } = options
// 這裡判斷有沒有從 Server 端帶來的資料 ⬇️
const initialState = pinia.state.value[id]
function setup() {
if (!initialState) {
if (isVue2) {
set(pinia.state.value, id, state ? state() : {})
} else {
pinia.state.value[id] = state ? state() : {}
}
}
const localState = toRefs(pinia.state.value[id])
}
}
解決跨請求狀態污染(Cross-Request State Pollution)的問題
在第一篇時我們有提到:跨請求狀態污染(Cross-Request State Pollution)。這裡一樣是為了避免污染的問題,另外也允許在 getter 裡面使用其他 store 的狀態。
const useB = defineStore({
id: 'B',
state: () => ({ b: 'b' }),
})
const useA = defineStore({
id: 'A',
state: () => ({ a: 'a' }),
getters: {
fromB(): string {
const bStore = useB()
return this.a + ' ' + bStore.b
},
},
})
const pinia1 = createPinia()
const pinia2 = createPinia()
setActivePinia(pinia1)
const aStore = useA()
// 模擬不同的 application
setActivePinia(pinia2)
const bStore = useB()
bStore.b = 'c'
aStore.a = 'b'
console.log(aStore.fromB) // 必須輸出 'b b'
這段程式碼模擬了 aStore 跟 bStore 分別屬於不同請求(不同請求有不同的 Pinia instance 跟 vue application),如果今天是在「跨請求狀態污染」發生的情況下 aStore.fromB 的值可能就不會是 b b。
讓我們逐步解析這段程式碼的執行步驟:
- 建立 Pinia instance 1,並且設定為當前的 Pinia instance。
- 建立
useAstore,並且設定為當前的 Pinia instance。 - 建立 Pinia instance 2,並且設定為當前的 Pinia instance。
- 建立
useBstore,並且設定為當前的 Pinia instance。 - 設定
bStore.b的值為c(初始值為b)。 - 設定
aStore.a的值為b(初始值為a)。 - 讀取
aStore.fromB的值觸發 getter function,並且回傳aStore.a + ' ' + bStore.b。- 執行
const bStore = useB()這個時候的activePinia是 Pinia instance 2 - Pinia instance 2 上的
bStore.b為c,所以回傳b c。
- 執行
因為遭受到了跨請求狀態污染,所以最終的結果與期望不符。要解決這個問題很簡單,我們只要在每次執行 getter function 時,都把 activePinia 設定為當前 scope 的 Pinia instance 就可以了。
function createOptionsStore(id, options, pinia) {
const { getters } = options
function setup() {
// ...
const localGetters = Object.keys(getters || {}).reduce((computedGetters, name) => {
computedGetters[name] = markRaw(
computed(() => {
setActivePinia(pinia) // ⬅️ 在這裡設定 activePinia
const store = pinia._s.get(id)
if (isVue2 && !store._r) return
return getters![name].call(store, store)
})
)
return computedGetters
}, {} as Record<string, ComputedRef>)
}
}
這時如果我們把 setActivePinia(pinia) 加回去的話,aStore.fromB 的值就會是 b b。
接續上述第 6 步驟的執行流程:
- 讀取
aStore.fromB的值觸發 getter function,並且回傳aStore.a + ' ' + bStore.b。- 這個時候的
activePinia是 Pinia instance 1,執行const bStore = useB()。 - Pinia instance 1 沒有
bStore,所以建立一個bStore。 - Pinia instance 1 上的
bStore.b沒有被修改過,為預設值b,所以回傳b b。
- 這個時候的
這樣就解決了跨請求狀態污染的問題!
結語
綜合以上的內容,我們可以整理出 Option Store 的實作內容:
- 初始化 state,這裡在初始化時需要考量 SSR 的問題,所以僅在
pinia.state.value[id]不存在時才會初始化 state。 - 整理 getters,這裡會使用
Function.prototype.call讓 getter 的this指向 Store instance,並且處理跨請求狀態污染(Cross-Request State Pollution)的問題。 - 合併 state、actions 跟 getters,並且使用
createSetupStore來實際建立 Store instance。
看完 createOptionsStore 的實作後發現裡面處理的事情非常單純,但礙於篇幅的關係,如果要在這一篇也交代完 createSetupStore 的實作細節內容會太長。因此將 Setup Store 的內容獨立出來,下一篇將深入核心研究 Setup Store 的實作細節。
參考資料
請我喝杯咖啡
如果這裡的內容有幫助到你的話,一杯咖啡就是對我最大的鼓勵。